The Autonomous Human Risk Management Platform
Replace manual security awareness programs with an AI engine that automates phishing simulations, training, and risk remediation.
Security awareness shouldn't be a compliance checkbox. PhishFirewall uses AI to automate training, eliminate administrative busywork, and measurably reduce risk. Give your team their time back while hardening your human firewall.
Tired of the endless cycle of ineffective training? So were we.
The Old Way:
A Familiar Story
For decades, security awareness has been treated as a compliance checkbox, not a strategic initiative. The result? Frustrated security teams, resentful employees, and zero measurable improvement in risk.
Bob
IT Director
"Drowning in manual overhead. Spending Friday afternoon setting up generic simulations instead of strategic initiatives."
Hover to solve
Fully Autonomous AI
The PhishFirewall Way
Bob went home early. Lora handled the simulation setup, scheduling, and remediation automatically.
Elizabeth
Accounts Payable
"Clicks a suspicious travel email because the 'one-size-fits-all' training never taught her about specific finance threats."
Hover to solve
Hyper-Personalized
The PhishFirewall Way
Lora recognized Elizabeth's role. She received a specialized 'Wire Fraud' simulation instead of generic spam—and she spotted it.
Joe
Sales Team
"Enraged by boring, generic phishing tests that waste his time. He ignores IT's emails and hates the 'gotcha' culture."
Hover to solve
Gamified & Positive
The PhishFirewall Way
Joe just earned a 'Cyber Rockstar' badge. He watched a 45-second, Netflix-style clip that actually respected his time.
The PhishFirewall Way:
AI-Powered, Personalized & Positive
PhishFirewall represents a strategic shift from a tool you manage to a solution that works for you. Our platform is built around an "agentic AI"—a fully autonomous agent named Lora.
Agentic Human Risk Management
Fully Autonomous AI Agent
Lora handles everything. She assesses users, deploys training, and runs simulations. Zero simulation management required.

Adaptive Learning Paths
A generic approach is an open invitation for a breach. Lora acts as a personal security tutor, tailoring simulations and training to each user's role, risk profile, and past performance.
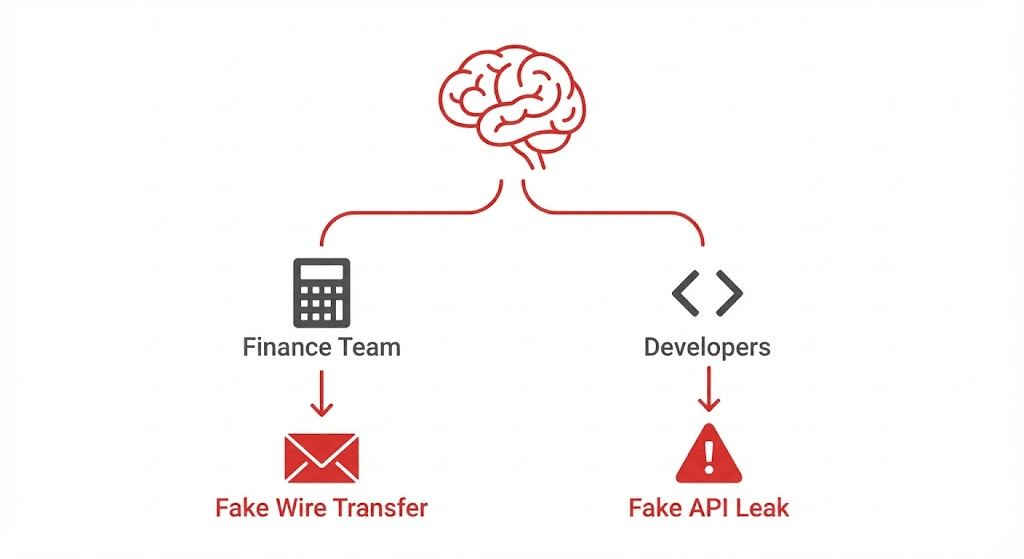
"Smart Reflexes"
Short, engaging, "TikTok style" videos (<60s) build subconscious reflexes, not just knowledge.
Click to see Lora in action ▶
Instant Feedback & Positive Reinforcement
We celebrate success and use mistakes as teaching moments. Elements like leaderboards, badges, and progress tracking boost motivation and friendly competition.
🎉 Cyber Rockstar!
Threat Reported Successfully
+50 Security Points
How It Works: Simple Setup, Powerful Automation
PhishFirewall is designed for maximum impact with minimum effort. Up and running in less than an hour.
1. Connect Your Environment
Securely sync your user directory (Microsoft 365 or Google Workspace) with a simple, read-only OAuth application.
2. Let Lora Take Over
Lora begins assessing vulnerabilities and deploying personalized simulations. No simulations to manage.
3. Measure Risk Reduction
Track progress via a single dashboard. Monitor click rates, reporting, and engagement in real-time.
The Science of Secure Habits
Traditional training fails because it ignores how habits are formed. PhishFirewall is built on proven psychological principles, like the BJ Fogg Behavior Model, to drive real behavior change. We focus on Motivation, Ability, and Prompts to make secure habits second nature, not an afterthought.
Building Reflexes, Not Checking Boxes
Annual training is forgotten in weeks. We build lasting security reflexes through a continuous cycle of realistic phishing simulations and bite-sized microlearning modules that fit effortlessly into the workday. This ongoing practice ensures your team is always prepared.
Security That Works Where You Work
The best security tools are the ones people actually use. By embedding tools like our one-click email reporting button directly into the employee's daily workflow, we reduce friction, increase participation, and turn your entire workforce into a human firewall.
The Difference is Clear
See why leading organizations are switching from legacy training to the PhishFirewall platform.

Our Commitment to Your Success
We don't just sell software; we deliver a partnership focused on measurable risk reduction.
Sub 1% Phish Click Rate Guarantee
We commit to driving your click rate below 1% within 12 months. If not, we provide free consulting to fix it.
90-Day Satisfaction Guarantee
Try PhishFirewall risk-free. If you're not satisfied within 90 days, we'll provide a full refund.
See What You Save When You Fire
"Check-The-Box" Training
Stop managing simulations. Start managing strategy.
IT Hours Reclaimed
332
hours per year
No more manual simulation setups, reporting, or chasing repeat clickers
Click Rate Drop
8% → <1%
in 12 months
From industry average to our guaranteed sub-1% rate
Employee Sentiment
Positive (97%)
user satisfaction
No more punitive training complaints—only positive reinforcement
These results are based on 500 employees
Get These Results for Your CompanyReady to See the Future of
Security Awareness?
Reclaim your time, end employee frustration, and build a genuinely resilient security culture.
Get Your Personalized Demo
Fill out the form below to see Lora in action.
The Complete Human Risk Platform
From autonomous training to AI-powered offensive security, PhishFirewall provides everything you need to secure your human layer.
Security Awareness
Autonomous training that reduces click rates to <1%.
Phishing Simulations
AI-driven lures adapted to every employee's role.
AI Pen Testing
Secure your AI models and data pipelines from new threats.
PhishEQ
Email security that retracts threats from the inbox instantly.
Risk Analytics
Deep reporting on human risk and behavior change.
Penetration Testing
Full-spectrum offensive security for modern enterprises.
Free Tools Hub
Check your risk for free with our suite of security tools.
Micro-Learning
Engaging, <60 second training in the flow of work.
Frequently Asked Questions
Ready to Secure Your Human Layer?
Join the hundreds of organizations that trust PhishFirewall.
- Free Risk Assessment
- Migration Plan Included
- No Credit Card Required
